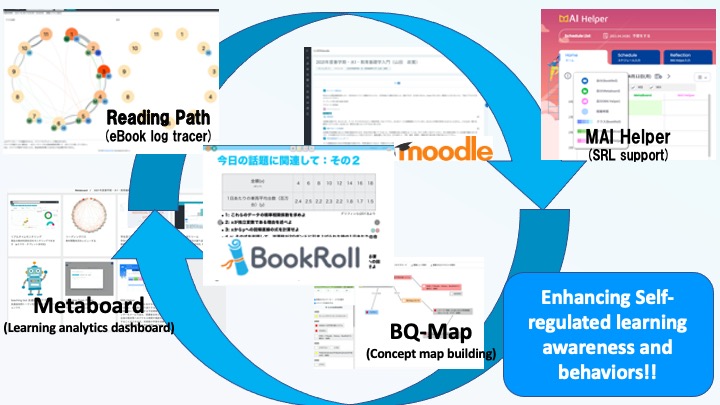
Development and evaluation of learning analytics infrastructure including learning material delivery functionality 2022-2025
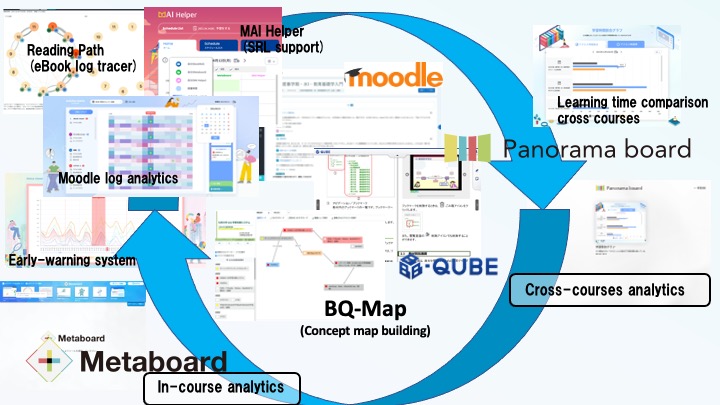
Dashboard research has become a major field in learning analytics research, but it is not enough to just create and evaluate dashboards using various algorithms. A dashboard is merely a visualization of the actions within that larger platform or content delivery infrastructure, such as a learning management system, where the original learning actions take place. There are many points that cannot be done without considering how the original learning management system, content delivery infrastructure, and other platforms should be designed, and there are many cases the platform itself needs to be reviewed when learning analytics is advanced and key learning behaviors become visible. However, in reality, learning analytics is often conducted with the platform in mind, and it is not always possible to modify the platform itself.
The point of this project is to focus on this point and to think about the opposite, rather than conducting unidirectional research to simply create dashboards that visualize learning behaviors on the platform. Think about how the design of the infrastructure should be, based on the results of learning analytics-related activities that represent dashboard development and evaluation, and then improve it, developing and evaluating an infrastructure that can turn the cycle of making learning analytics better and supporting learning analytics. The objective is to develop a dashboard design model that supports learning analytics. This research is supported by JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research, Kiban Kenkyu A (general), under the direction of Dr. Yamada.
Development and evaluation of a learning dashboard to support decision making for learning behaviors 2021-2023
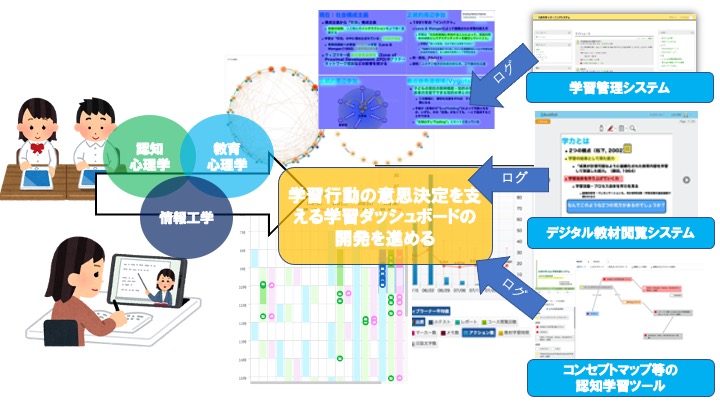
I believe that the decision to learn or not to do so ultimately depends on the each learner. From primary and secondary education, teachers have been providing various interventions for learners’ learning, but in the end, it is the learner’s problem to decide whether or not to learn and to act on it. But It is the desire of teachers to support learners’ decision-making and promote self-regulated learning. This research project aims to design, develop, and evaluate a learning dashboard that activates metacognition, one of the elements that support learners’ decision-making. This research is funded by the JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research, International Collaborative Research Acceleration Fund (B), in collaboration with Dr. Stephanie Teasley, University of Michigan.
Definition of educational data literacy and construction of a model for its development 2021-2024
In recent years, the development of learning dashboards and other tools that utilize the vast amount of learning logs accumulated in learning support systems has been underway. This is an active research field, and has been a major topic at the Learning Analytics and Knowledge (LAK) conference, an international conference specializing in learning analytics. It is good to visualize the results of analyzing learning logs, such as dashboards, and provide feedback to learners and faculty, but it is the learners, faculty, or users who look at the visualized results and think about what to do with them. The purpose of this research is to organize the elements of the abilities related to educational data literacy and to construct a model for developing such abilities.
Research funded by JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Exploratory Research (Pioneering Research) (I will serve as the PI)
Develop a feedback infrastructure that blends data-driven and knowledge-driven 2020-2023
Learning environments that take advantage of information and communication technologies have become widespread in recent years, and systems that fully utilize AI to support learning are also emerging. One of the key elements of learning support is feedback. Feedback on how learners have learned and what they should do in the future will change the face of learning. However, looking at the field of education and learning to date, teachers and other educators and learning supporters have provided feedback, and feedback provided by experienced educators is of high quality and will undoubtedly lead to better learning in the future.
This research is an attempt to integrate not only data-driven feedback by information and communication technology, but also knowledge-driven feedback by theory and experience. The empirical environment is a seminar-like small group learning environment where various types of feedback occur.
This research is being conducted as a JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research B (led by Dr. Yoshiko Goda, Kumamoto University).
Developing a Learning Analytics Platform Using Educational Big Data 2016-2020
The use of ICT is gaining acceptance and popularity in education, and a major benefit of using ICT is the ability to record learners’ learning activities. By utilizing this record, it is possible to derive information such as where learners are stumbling, how they are learning, and when they are learning, and to provide optimized learning support for each learner. In addition to learning support, it is also expected to improve teacher-led classes by providing feedback to instructors on the results of analyzing the learning records of students in the class. This field of research is called learning analytics, and it is spreading worldwide. The goal of this research is to develop and evaluate a learning analytics platform that connects primary, secondary, higher and adult education. Dr. Ogata (Kyoto University) is the Principal Investigator (Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas, S), and I am involved in this research as a sub-researcher.
Project Learning Support System for Visualizing Social Presence

Social presence is simply defined as “the sense of being aware of or being made aware of the presence of another person in front of you” even in computer-mediated communication (CMC), where the other person is not visible to you. While humans communicate face to face by incorporating their own emotions, such as facial expressions and tone of voice, it has been said that this is difficult to do in situations where the other person is not visible, such as in text-based CMC. However, since the early 1990s, in the field of social psychology, research about social presence in CMC was activated, and some of those research shows that social behavior, such as the relationship establishment, takes place through emotional communication even in CMC. In the late 1990s, some of research began to present that social presence is strongly related to the uttered content, and there is a growing view that even in e-learning, the strength of social presence depends on the uttered content. Social presence is said to have an educational effect on forming a good group, especially in group learning such as cooperative learning, as well as on cognitive activities related to learning. C4α extends “C4″, a system developed in past projects, by extracting only those statements that are related to social and cognitive presence, and then visualizing the situation within the group. The system also aims to support active project learning by providing a concept map creation tool, a chat tool to support social presence comments, a tool to grasp the login status of the other party, and a project management tool to manage tasks within the group. The system in this project is also being developed as a plug-in for Moodle. Collaborative research funded by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research.
Learning Analytics Research in Multi-generational Co-creation 2017-2019
In Japan, it is estimated that the population over 65 years old will account for 23% of the total population in 2010 and close to 30% by 2020. With a truly super-aging society, a variety of social life supports will be required. We believe that it is desirable to develop active seniors and to utilize the rich experience of the elderly in order to achieve social development. This research aims to extend the learning analytics platform to support multi-generational co-creation and social activities as a way to build a multi-generational co-creation society centered on the elderly. This research project (JST Future Society Creation Project) is led by Dr. Kizane (Kyushu University) and conducted as the research of the Learning Analytics Center.
Development and Evaluation of a Multi-Country Cooperative Learning Support System (COIL) 2014-2017
In recent years, an increasing number of universities have begun to offer cooperative learning programs with faculty members and students from overseas universities to develop global human resources. COIL is an educational format that promotes cooperative learning in foreign languages in cooperation with overseas universities. As part of support for study abroad, COIL with faculty and students in advance can be expected to help students adjust to their study abroad environment. However, in order to conduct COIL with overseas universities, there are many things that must be facilitated, including not only the design of the environment and content, but also time difference issues, cross-cultural understanding, language skills, and so on. The purpose of this study is to examine the facilitation required when conducting cooperative learning with overseas universities, develop a system that helps such facilitation, and evaluate the system. Joint research with Dr. Goda (Kumamoto University), Dr. Ishige (Otemae University), and Dr. Handa (Saitama Institute of Technology), funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research.
Project for the development of teaching materials for university librarians who want to support learning "ILI-L" 2014-2017
This project is the successor to the ILI-L Librarian Development Project, which is described in the “Past Projects” section, and is ongoing with a research grant. We will continue to develop instructional materials that contribute to the development of knowledge and skills related to learning support, in line with the findings of instructional design and learning science. We plan to increase the content and incorporate mechanisms that can be used in the work of university librarians. We are developing a joint research project (completed) with Dr. Watanabe (Kyushu University), Dr. Goda (Kumamoto University), and Dr. Maskawa (Shizuoka University), funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research.
Development and Evaluation of a Game-Based Learning System for Learning to Use the Library 2015-2016

This study develops and evaluates a game-based learning system for students who do not know how to use the library. The ARCS model, a type of instructional design, was used as the design of the game, and the development was based on an analysis of seminars and teaching materials that have been held in university libraries in the past. The game is activated on a smartphone, and the user actually explores the University’s library while completing the game. A joint research project between Dr. Kaneko (Kyushu University) and members of the University Library (Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Budding Researchers, Grant-in-Aid for Public Interest from the Foundation for Fusion of Science and Technology).
Development and Evaluation of Game-Based Learning Environments Outside the Classroom 2015-2016
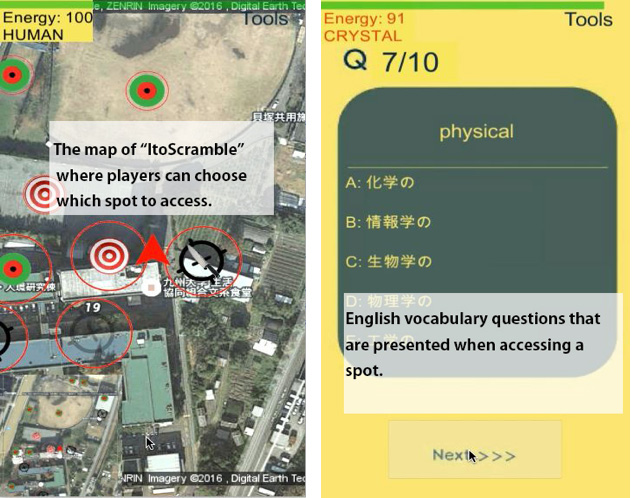
This research project started with the aim of developing and evaluating a game-type learning environment to make learning outside the classroom more effective. The game is divided into two teams, and the game displays English words related to a certain place, and students answer the meaning of the words. If the students exceed a certain percentage of correct answers, they are awarded a spot in that “place” in the game. Formative evaluation showed that there was an effect on word acquisition. Collaborative research with Dr. Okada (Kyushu University) and Dr. Kaneko (Kyushu University), funded by JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Exploratory Research (Budding Researchers).
Development and Evaluation of a Flipped Classroom Support System Incorporating the Knowledge Construction Jigsaw Method 2014-2016
The term “flipped classroom” or “flipped learning” is spreading both in Japan and abroad. The term “flipped classroom” refers to the practice of conducting classes that encourage deeper learning by building on the content of lectures, answers to example problems, and other aspects of learning input that have been conducted in class in the past as prior learning homework, and then building on this homework in the classroom. The concept is not so new as to be surprising, but with the advent of ICT, it has become possible to grasp the learners’ prior learning status before the class, to change the class design based on the grasped content, to shoot lecture videos in advance and provide them to the learners, and to provide the students with the lectures. The ability to utilize open education content such as OCW, YouTube.Edu, and MOOCS is a difference from the past. In this study, we will develop and evaluate a system that incorporates the jigsaw method from the stage of doing that pre-assignment, supports the creation of expert groups and jigsaw groups, and also supports the exploration of teaching materials and their assignment to learners. Joint research with Dr. Yasunami (Kumamoto University), Dr. Goda (Kumamoto University), Dr. Matsukawa (Osaka University), and Dr. Hata (Otemae University), funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research.
ILI Librarian Development Project 2012-2013
Today, the role of libraries is changing dramatically by the spread of the view of universities as open to society, libraries as places for learning, and the digitization of books. In line with this era, the competencies required of library staff are naturally changing. However, due in part to reductions in the number of library staff at universities, the current training of library staff, while recognized as necessary, is not being implemented well. This project will train library staff to meet current needs. I will be involved in the project in terms of the creation of training programs and e-learning of learning content. Project grant from the Foundation for Library Promotion A collaborative project among Nagoya University Library, Shizuoka University Library, and Kanazawa University Library.
Development and Evaluation of Mentoring Support System Based on Self-Regulated Learning Theory 2012-2015
This is continuous research of a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research project led by Dr. Hiroyuki Miyagawa of Aoyama Gakuin University. The mentoring support system based on the self-regulated learning theory, which we have been working on until last year, is a system that estimates the degree of self-regulated learning of students based on the value calculated from a questionnaire that indicates the degree of self-regulated learning in online learning and support mentors with a function to estimate learners who need support and a function to provide them with a support based on the mentoring guideline in the planning stage of learning in the self-regulated learning cycle. However, although we were able to reduce the workload of the mentors, who are the learning supporters, to some extent, the key part of improving the learner’s self-regulated learning was still insufficient. In this project started in FY2012, we plan to develop and evaluate a system that aims to increase the learner’s self-regulated learning level as well. Collaborative research with Dr. Miyagawa (Aoyama Gakuin University), Dr. Kato (Open University of Japan), Dr. Goda (Kumamoto University), Dr. Matsuda (Shimane University), and Dr. Saito (Aoyama Gakuin University), funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research.
Development and Evaluation of "C4″, a Foreign Language Learning Support System for Activating Social and Cognitive Interaction 2011-2013
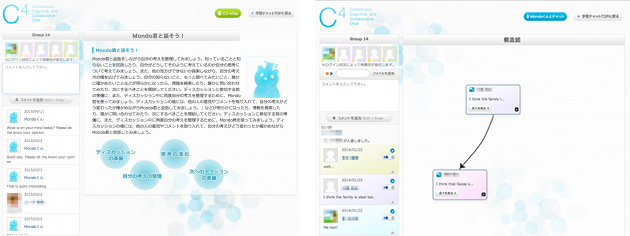
The purpose of this research is to develop and evaluate a foreign language learning support environment outside of the classroom. In foreign language education, it is difficult to achieve mastery goals in university classes alone, so learning outside of class is important. Also, In recent years, there has been a growing need to create an environment that provides learning opportunities outside of the classroom in line with the original purpose of foreign language education, which is to motivate students to learn and to “think about something using English”. In this study, we developed and evaluated a cooperative foreign language learning support system “C4 (Sequad),” which incorporates not only social interaction among learners, but also support for building human relationships and deepening thinking about a given topic using English. The system has been developed and evaluated as a module of Moodle. Collaborative research with Dr. Yasunami (Kumamoto University), Dr. Goda (Kumamoto University), Dr. Hata (Otemae University), and Dr. Matsukawa (Osaka University), funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research. The results of this research project received the Best Paper Award at ICWL2014.
IDO" Project, a cooperative learning support system focusing on the "frog-in-the-well" effect, 2009-2012
“frog in the well” effect is the effect of utilizing the academic self-concept. For example, a student’s academic self-concept in English may be based on his/her subjective evaluation of his/her own English ability by the average score given by the teacher and the test scores of his/her friends during the in-class tests. This is exactly when the academic self-concept is formed. Such an effect of academic self-concept brought about by social comparison is called the “frog in the well” effect.” The “IDO” system conforms to the “frog in the well” effect and supports cooperative learning by automatically creating groups that can form a positive academic self-concept of themselves based on their test scores. Joint research with Dr. Yamauchi (University of Tokyo), Dr. Kitamura (Tokyo Keizai University), Dr. Misono (Shimane University), and Dr. Matsukawa (Osaka University), funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research.
Development of a Mentoring Support System to Facilitate Self-Regulated Learning in e-Learning 2009 - 2012
We are conducting research on a mentoring support system that promotes self-regulated learning in e-learning. A major challenge in e-learning has been the lack of continuity in learning, which is based on the assumption that there are almost no face-to-face lectures. For this reason, it is said that it is necessary to provide emotional and other support to learners, such as appropriate mentoring by a mentor. However, the workload for the mentor is very high because he or she is required to keep track of the learner’s situation and respond as quickly as possible. It is also problematic to train learners who cannot learn without a mentor. Based on the above two problems, this study focuses on the self-regulated learning theory, and develops and evaluates a mentoring support system to support learners’ self-regulated learning attitude and behavior. Joint research with Dr. Miyagawa, Dr. Matsuda, Dr. Saito (Aoyama Gakuin University), Dr. Kato (Open University of Japan), and Dr. Goda (Otemae University), funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research.
Conomi+ 2008 - 2009

Conomi+ is an English learning system designed to make it easy for students to study English at home or outside of school. The system uses collaborative filtering, a recommendation algorithm used by Amazon.co.jp and others, to deliver English news that matches the learner’s interests, and provides cognitive and social learning support such as dictionary functions, word registration, and comment input, so that students can continue learning even outside of school. The system is designed to support students to continue their learning outside of school. In the second phase, we developed and evaluated a new collaborative filtering algorithm that “recommends items that are not a perfect fit but are of some interest. Compared to conventional collaborative filtering, the results showed that it produced a wider range of news genres to read and better learning outcomes. I was responsible for the overall design of the system, part of the evaluation, and the direction of the project. The project was conducted by the Benesse Chair of Advanced Educational Technology in the Interfaculty Initiative in Information Studies, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary Information Studies, the University of Tokyo (supervised by Dr. Yuhei Yamauchi, Associate Professor at the University of Tokyo). The results of this research have been accepted for publication in Educational Technology Research & Development.
Examining the Effects of Social Presence and Cognitive Presence on Task-Based Foreign Language Learning 2008- 2009
In remote learning, it has been claimed that feeling the presence of other learners around you can be effective in the affective aspects of learning, such as increasing motivation to learn and satisfaction with learning. Although there are many practices of remote learning in foreign language education, most of those studies have been conducted without considering the background theories of learning science and psychology related to remote education. In this study, we focused on “presence” in task-based foreign language education in order to examine the method of linking a sense of the other’s presence to actual learning (individual research). The results of this research were accepted for publication in Computers & Education. Research funded by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research
English de Career Development 2008

English de Career Up is a spin-out project of “NARIKIRI English! In order to disseminate the research results of “NARIKIRI ENGLISH!”, we have made it available via podcasting instead of Willcom’s W-zero3. English de Career Up mainly targets those who work in the IT industry. The materials were selected through interviews with people working in IT companies and were developed using English vocabulary and expressions frequently used on English web pages of IT companies, as well as specialized vocabulary and expressions. This was a joint research project between the University of Tokyo and Benesse Corporation. I was engaged in selecting the work and planning the stories. Featured in Nikkei Net, Nikkan Kogyo Shimbun, ITMedia, and many other media. iTunes Podcasting #1 for 8 consecutive weeks! (The service has now been terminated.)
Narikiri English! 2006 - 2008

We develop and evaluate English listening materials tailored to the context of learners’ English use. The system that runs the teaching materials uses Willcom’s W-zero3. In FY2007, we developed and evaluated the effectiveness of the program for Nippon Steel Corporation employees. In fiscal 2008, we conducted an analysis and verification of the effectiveness of the program. The results of the comparison between the sales and non-sales representatives targeted by “NARIKIRI ENGLISH!” showed no difference in growth in English ability, but a delayed survey conducted two months later showed that the sales representatives were able to use expressions from “NARIKIRI ENGLISH! The results showed that the program contributed to a subjective sense of efficacy in terms of improvement in practical skills. I was mainly responsible for the design and development of the system. The project was conducted by the Benesse Department of Advanced Educational Technology, Interfaculty Initiative in Information Studies, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary Information Studies, the University of Tokyo (supervised by Associate Professor Jun Nakahara of the University of Tokyo).
Research on English Communication Skills Development Support System Using Synchronous CMC 2003 - 2008
This research was conducted throughout my master’s and doctoral programs. Computer-mediated communication (CMC) tools are real-time communication tools such as text chat and video conferencing, which are called “synchronous CMC. This research examines the effects of synchronous CMC and learners’ video and audio on communicative learning in a foreign language, and how a language education system should be designed. Research funded by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research
International Comparative Study on Information Morale
Data on information technology and information morals was collected from educators around the world and analyzed. The study reports on the use of cell phones, parental responsibility, and teachers’ attitudes and efforts toward learners with poor information morals (Principal investigator: Prof. Kanji Akahori, Tokyo Institute of Technology).
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Model Project for Promoting Sharing of Educational Information "e-Teacher Project" 2003 - 2004

The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) has been implementing a model project (“Model Project for Promoting Sharing of Educational Information”) since FY2003 with the aim of expanding the circle of teachers of the same subject and encouraging teachers to voluntarily improve their IT teaching skills. We had built and operated a website for sharing class case studies to disseminate the research results of research groups in each region designated for this model project to teachers nationwide. After 2005, the project management was transferred to Mitsubishi Research Institute, Inc. and was successfully completed (Project Planning and Evaluation Committee Chairman: Professor Kanji Akahori).